Benefits of Elastin
Elastin protein is a vital part of many tissues in the body, and elastin structure gives the protein several benefits. Unfortunately, elastin levels can decline for various reasons, leading to multiple concerns. Read on to learn more about the benefits of elastin and how elastin supplements may be beneficial for restoring protein levels throughout the body.
Where Is Elastin Found in the Body?
Elastin is a protein that your body manufactures from tropoelastin, an amino acid made by endothelial cells. These cells are also responsible for producing another essential structural protein called collagen. Once manufactured, elastin becomes a key component in your:
- Bladder
- Lungs
- Large blood vessels
- Some ligaments
- Skin
- Cartilage
What Does Elastin Do?
The primary function of elastin fibers is to allow tissues and organs to stretch. Depending on its location, elastin functions in different ways.
Elastin in the Bladder
Your bladder is the organ that stores urine produced by the kidneys until you release it through your urethra during urination. Urine levels fluctuate throughout the day and night, so your bladder must be able to stretch to accommodate more liquid and then return to its standard shape once empty. Stretchy elastin protein fibers help with this process.
Elastin in Ligaments
Ligaments are the type of connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. In some ligaments, elastin protein fibers help the connective tissue stretch to accommodate your movements.
Elastin in Lungs
When you breathe, your lungs expand and contract to help move air in and out of your respiratory system. In the lungs, the function of elastin fibers is to allow the lungs to move outward and accommodate incoming air without stretching too far.
Elastin in Skin
Elastin in the skin contributes to the overall elasticity of your skin tissue. It makes skin resilient and able to stretch when you make facial expressions. In the skin, the function of elastin is complemented by the actions of collagen, which supports the tissue. Together, elastin and collagen give skin its youthful firmness and suppleness.
Elastin in Arteries and Veins
In large arteries and veins, elastin is essential to vascular function. Arterial elasticity allows blood to move through the cardiovascular system more freely. This helps the heart function properly and ensures blood can travel to and from the extremities efficiently.
What Causes Loss of Elasticity in Arteries, Veins, Lungs, and Skin?
Several things can result in a loss of elasticity in the arteries, skin, and the rest of the body. Typically, this happens when elastin fibers become damaged, or the body does not produce enough of the structural protein. Some things that contribute to lost elasticity include:
- Age: Elastin and collagen production rates naturally decline due to the aging process. Due to age, drops in elastin and collagen manufacturing are partially responsible for the development of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Oxidative stress: Highly reactive particles called free radicals found in ultraviolet radiation and pollution can cause oxidative damage that destroys healthy elastin protein fibers. This can cause signs of aging to develop prematurely and damage the cardiovascular system and other organs in the body.
- Atherosclerosis: This plaque accumulation inside the arteries is often caused by diet, lack of exercise, and smoking. When plaque builds up, elastin fiber levels may drop, leading to a loss of elasticity in the arteries that can raise blood pressure levels and increase your risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Emphysema: Smoking can cause this lung disease where elastin in the lungs breaks down, leading to symptoms like fatigue, wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
- Genetic disorders: People with genetic variations may develop conditions linked to low elastin levels, such as the heart defect supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS), the development disorder Williams syndrome, and the skin disorder cutis laxa.
How To Restore Collagen and Elastin
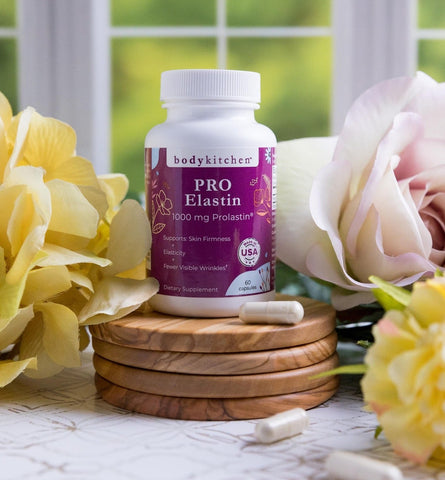
While restoring lost or damaged collagen and elastin completely may not be possible, you can potentially support the production of the structural proteins with supplements like Body Kitchen Pro-Elastin. Taking elastin supplements may supply your body with raw materials that can be used to manufacture new elastin fibers to potentially address the loss of elasticity in the arteries and elsewhere in the body.
In addition, you can take steps to protect existing collagen protein by:
- Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 every day. When you're outside for long periods, reapply sunscreen every two hours or more frequently if you're sweating heavily or swimming.
- Eating a well-balanced diet rich in leafy greens, berries, nuts, citrus fruits, and berries
- Following a skincare routine with products that contain antioxidants and ingredients that may lessen the damage caused by free radicals
- Quitting smoking to shield your body from the effects of chemicals found in cigarettes
- Increasing your physical activity to support circulation and overall health and well-being