The Science Behind Collagen and Elastin: How They Work Together for Youthful Skin
The Role of Collagen and Elastin in Skin Health
Collagen and elastin are two types of proteins that are found throughout the body, including in the skin. Both elastin and collagen are thought to be essential for skin health, but the two proteins may have different (though related) functions:
How Collagen Supports Skin Health
Not only is it possible for collagen to make up approximately 75 percent of the skin, it is also thought to be so abundant that it constitutes roughly a third of all the protein in the human body.1 It’s no surprise that such an abundant protein may be so important for the function of the tissue that it makes up, the importance of collagen for skin health is often difficult to overstate.
Collagen may provide structural support for the skin (as well as organs, tendons, bones, and ligaments).2 This means that skin that contains plenty of collagen is typically firm and plump, with a healthy and youthful appearance.
As we age, our collagen seems to tend to break down. Our bodies may create their own collagen, but the process may become less efficient and effective with aging, especially due to issues with nutrient absorption, which often leads to wrinkles and loose skin. In response, some people increase their collagen intake (through foods and/or supplements) in order to support the body’s production of new collagen and increase the health of the skin.
Science may support the use of collagen supplementation to increase skin health, reduce wrinkles, and improve skin texture.3 For instance, a systematic review of 26 randomized controlled trials (i.e., high-quality study designs) found that collagen supplementation may have resulted in significant increases in skin hydration and elasticity compared to the placebo group. 4
The Role of Elastin in Skin Flexibility
Not including the skin’s fat and moisture content, elastin protein is estimated to constitute between 2 and 4 percent of the skin in most adults.5 In particular, elastin may be crucial for skin elasticity, as well as tissue elasticity throughout the body (e.g., blood vessels, lungs, ligaments, cartilage in the ear, etc.) - in a systematic review of 26 randomized controlled trials, elastin has been shown to allow tissues to stretch out and shrink back without being permanently deformed by movement.
This is why, similar to a lack of collagen, a lack of elastin in the skin may also result in wrinkles and fine lines.6 This occurs since plenty of elastin is thought to be needed for the skin to bounce back to its neutral shape after movement and wrinkling. In the presence of a lack of elastin in the skin, repeated skin movement (that is, over many years) may result in wrinkles and sagging.
Similar to collagen, older people tend to have much less elastin in their skin than younger people. One may “test” the elastin content of their skin in an informal manner by pinching the skin on the back of one’s hand. Once the pinch is released, those with lots of elastin in the skin commonly find that their skin bounces back into its original shape very quickly, but in those with low elastin content, this may take a few seconds.7
How Collagen and Elastin Work Together in the Skin
A comparison of collagen vs. elastin will typically reveal that these two proteins may have distinct functions. Collagen may provide strength and structural integrity to the skin, while elastin may allow the skin to stretch and bounce back to its normal shape.8 (This is why it’s no surprise that elastin may be an estimated 1,000 times more stretchy than collagen.9 )
Despite the notable differences in elastin vs. collagen, the functions of these two proteins in the skin are commonly, but inextricably, related, as both the supportive framework of collagen and the stretchiness of elastin are thought to both be essential for skin health. For those concerned about wrinkle prevention and tightening the skin, prioritizing both proteins may be important.
Boosting Collagen and Elastin Production
As the body’s production of these two crucial skin proteins decline, increasing intake of collagen - and elastin-rich foods and supplements may improve skin health by providing the amino acids needed to produce them both. Another dietary strategy also involves increasing antioxidant consumption to neutralize free radicals that may otherwise contribute to breakdown of collagen and elastin in the skin.
A nourishing diet that includes sources of gelatin such as bone broth as well as fatty fish, eggs, lean meats, nuts, beans, berries, and leafy green vegetables is one way that may support the body’s collagen and elastin production.10
In addition, avoiding behaviors that contribute to collagen and elastin breakdown may help maintain skin health. The behaviors to avoid include cigarette smoking, tanning and sun exposure, as well as exposure to air pollution. To possibly protect the skin, quit smoking, wear sunscreen every day, if possible, exercise on a regular basis, and avoid air pollution (e.g., by using an air purifier).11
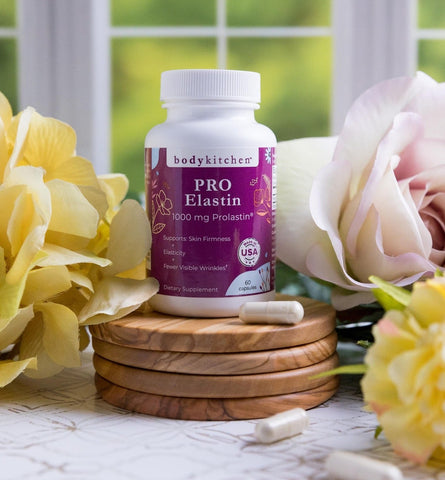
The Best Collagen and Elastin Supplement: Body Kitchen Collagen + Elastin Powder
If increasing dietary intake of collagen and elastin prove to be insufficient for your skin health goals, one may want to consider taking elastin and collagen supplements as a more effective and targeted addition.
Rather than seeking out the best elastin supplement or the best collagen supplement, consider using a supplement that contains both, for efficiency and affordability: Body Kitchen’s Collagen + Elastin Powder. Despite the fact that there are thought to be hundreds of collagen supplements available for purchase, very few of these options may also incorporate elastin, setting Body Kitchen’s product apart from the alternatives. This powder is also completely unflavored and extremely concentrated, which means that you may mix it into virtually any beverage without affecting its taste or texture.
Each serving of the Collagen + Elastin Powder can contain 2,500 mg of ultra high-quality Verisol® Collagen. Not only may this grass-fed form of collagen be extremely bioavailable and bioactive, but its benefits have been thought to be demonstrated in clinical studies with up to 30 percent increases in skin elasticity, 65 percent increases in collagen activity, and 32 percent reductions in eye wrinkles.
As for the elastin in this product, each serving offers 250 mg of Pro-lastin®. This is a peptide form of marine elastin that is commonly harvested from the coast of France. The peptide form of elastin has been thought to be developed to maximize digestibility as well as bioavailability.
Each dose of Body Kitchen’s pure, concentrated protein powder may also offer 100 percent of the daily recommended intake of vitamin C. This key antioxidant may reduce oxidation throughout the body, minimizing sun damage, which means it may also help improve skin health. In addition to the vitamin C content, there is 100 mg of hyaluronic acid inside, which may attract and hold onto moisture in the skin to provide “plumping” effects similar to filler (thereby reducing wrinkles and sagging).
Talk to a Medical Professional Before Adding a Collagen and Elastin Supplement
Collagen and elastin supplements such as Body Kitchen’s are widely believed to be safe for most people. However, certain groups may be at greater risk of side effects from this supplement. For instance, those with fish, shellfish, or egg allergies may be more likely to have an allergic reaction to a collagen/elastin supplement. Similarly, those who need to reduce their protein intake (e.g., those who have a history of gout) should possibly avoid taking protein powder supplements. In addition, keep in mind that collagen and elastin supplements may cause digestive side effects, such as diarrhea or nausea. Either way, before beginning to take these supplements, it’s typically recommended to speak to a qualified medical professional to be sure that it’s a good fit for your medical situation.
References
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23089-collagen
- https://dermnetnz.org/topics/collagen
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8824545/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10180699/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22482-elastin
- https://www.eucerin.co.uk/skin-concerns/ageing-skin/loss-of-elasticity
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22482-elastin#function
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7474469/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22482-elastin
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22482-elastin
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22482-elastin