Does Adding Collagen to Coffee Make It Healthier?
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a category of protein that makes up about 30 percent of the protein in the human body. This includes 75 percent of the skin (when it is at its youngest and healthiest) as well as a significant fraction of the muscles, bones, cartilage, tendons, and blood.
Collagen is necessary as a structural support and protection for numerous organs and body parts, as well as for the growth of new skin cells, blood clotting, and numerous other essential functions throughout the body. It is also important for hair and nail growth, skin elasticity, and joint and bone health.
Health Benefits of Collagen
While more high-quality studies will be needed to demonstrate all of collagen’s benefits, early research suggests that collagen supplementation (and/or a diet high in collagen) could have a number of health benefits:
Skin Health
Taking a collagen supplement, such as a collagen peptide powder, by mouth is shown to improve skin health, reduce wrinkles and improve skin’s texture. A systematic review of existing research on collagen supplementation and skin health found that it may create significant improvements in skin hydration and elasticity.
Hair and Nail Growth
A study of the effects of fish collagen peptides on human cells in vitro and on mice, found that collagen could potentially be beneficial for those with alopecia, reducing hair loss and increasing hair regrowth.
Likewise, collagen supplementation is believed to increase the growth and strength of nails, with one study showing that supplementing with bioactive collagen peptides increased nail growth rates by 12 percent and decreased subjects’ instances of broken nails by 42 percent.
Joint Support
Collagen supplements may also help support the health and function of joints. Depending on the form of collagen you take, the peptides may be able to be transported by the body to the joints, reducing pain and inflammation. Keep in mind though, that collagen supplementation is not an instant fix; for those with osteoarthritis, for example, you may need to supplement with collagen for up to five months before your joint symptoms begin to abate.
Bone Density
Certain types of collagen peptides have demonstrated benefits for bone density. For instance, in a high-quality study of 131 postmenopausal women (a group that tends to struggle with decreased bone density), taking specific collagen peptides (SCP) increased formation and reduced degradation of bones, thereby increasing subjects’ overall bone mineral density.
Frequently Asked Questions About Collagen and Coffee
Does Heat Destroy Collagen Powder?
Since many people drink coffee daily, they commonly consider adding collagen to coffee as an easy way to consume this powdered supplement.
But could the exposure to high temperatures destroy the collagen peptides, reducing or even erasing the health benefits? After all, high temperatures can denature proteins, causing minor changes to their molecular structures.
A study in which researchers exposed collagen to temperatures ranging from 302 to 788º F (150 to 420º C) found that it began to break down starting at about 302º F. But coffee rarely gets this hot, with most people brewing it at around 195 to 205 ºF (90 to 96ºC). As long as you let your coffee cool to well below 300º F, there shouldn’t be any issues with the temperature of the liquid breaking down your collagen powder.
Does Adding Collagen Supplements to Coffee Enhance Its Benefits?
Knowing that collagen added to coffee is unlikely to be affected by normal brewing temperatures may prompt curiosity regarding the benefits of collagen in coffee. Unfortunately, while consuming collagen powder in coffee has no notable downsides, it also doesn’t have any major benefits.
If it’s convenient, it makes sense to take powdered collagen in coffee. But it’s just as beneficial to mix collagen into tea, smoothies, juice, oatmeal, soup, or other common foods and drinks that stay well below that threshold of 302º F.
Does Coffee Deplete Collagen in the Body?
While coffee does not deplete collagen, it may slow down the body’s rate of collagen production. This is due to the fact that caffeine inhibits the enzyme prolidase, which is essential for the body to synthesize more collagen.
Keep in mind that our bodies break down caffeine with an enzyme called CYP1A2, and depending on our genes, we may produce different amounts of this enzyme. This means that the degree to which caffeine affects collagen production depends on one’s genetic makeup.
Either way, consuming a few cups of coffee per day is likely to have a minimal effect on overall collagen levels.
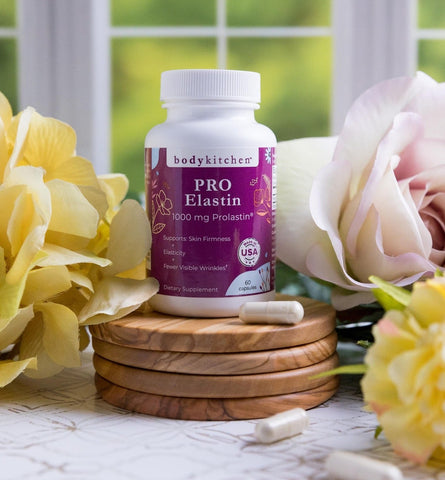
The Best Collagen Powder: Body Kitchen Collagen + Elastin Powder
One of the best collagen supplements currently available on the market is Body Kitchen Collagen + Elastin Powder. It contains a combination of not only 2,500 mg of high-quality collagen but also 250 mg of elastin, which work together to promote skin health and resilience.
To be more specific, the collagen in this supplement is called Verisol® Collagen, which comes from grass-fed sources and has been demonstrated to increase collagen activity by 65 percent, increase skin elasticity by 30 percent, and reduce wrinkles around the eyes by 32 percent. Meanwhile, the elastin is called Pro-lastin®, a form of pure marine elastin that comes from the coast of France and that is in peptide form to increase its bioavailability and absorption.
Body Kitchen Collagen + Elastin Powder also provides 100 percent of the daily recommended dose of antioxidant vitamin C, which is necessary for producing collagen and elastin and is also thought to reduce sun damage. It also has 100 mg of hyaluronic acid, which may pull moisture into the skin to increase its hydration and smoothness. 1
Speak with Your Doctor Before Taking Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplementation is safe for most people but could be an allergy risk for those who are allergic to eggs, fish, or shellfish. It may also be inappropriate for those who need to consume a low-protein diet for health reasons, such as those with a history of gout. Before incorporating collagen supplementation into your daily routine, speak with your doctor to confirm they it is appropriate for your unique medical situation.
References:
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23089-collagen
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6835901/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8824545/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10180699/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9569759/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28786550/
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/collagen-health-benefits
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5793325/