What is the Function of Collagen?
Collagen is one of the most essential substances in the body. As a matter of fact, it is the most abundant protein in our bodies It is found in many different systems, from your veins and arteries to your joints, skin, and even hair follicles. Collagen is an extraordinary protein with a unique structure: it consists of long strings of amino acids that form tight coils. This unique structure gives collagen a springy, resilient consistency. It’s used by the body to make structures that are both flexible and strong.
Functions of Collagen
Collagen has many vital functions in different parts of the body. Here are some of the most important:
- Function of collagen fibers in connective tissue: Collagen fibers hold your body together. It’s found in every type of connective tissue, from the membranes that protect your brain to your ligaments and tendons.
- Function of collagen in muscles: Collagen helps give your muscles their flexibility and strength. Without sufficient collagen, your muscles can become weaker. Additional collagen can help improve muscle strength and athletic performance.
- Function of collagen in bone: Your bones consist of a calcium compound (hydroxyapatite) and organic materials, principally collagen. Collagen may make up almost 30 percent of your bone tissue. It gives your bones their strength and resiliency. As well as the bones themselves, collagen is also used to build the tissues that make up your joints.
- Function of collagen in the skin: Of all the tissues in your body, the deep layers of your skin have the highest proportion of collagen. Together with elastin, another protein, collagen is the substance that gives your skin its structure and pliability. Your skin needs collagen to stay young-looking and smooth.
- Function of collagen in blood vessels: Collagen is found in the walls of your blood vessels, from the largest veins to the smallest capillaries. Your blood vessels need to be strong and flexible so that they can expand and contract as they transport blood throughout your body. If the walls of your blood vessels weaken, you can experience many circulatory issues.
Boosting collagen levels
All the collagen that your body uses to make these important structures is produced from amino acids in your diet. Until you’re about 25, your body has no problem producing all the collagen you need to stay fit and healthy. As you get older, however, your body starts to produce less collagen. It’s, therefore, less able to build and maintain the tissues and structures that require this protein. For every year over 25, your collagen production may drop off by as much as 1%. For women who’ve gone through menopause, the decline may be even more rapid. Even if you’re still under 25, you might benefit from boosting your collagen levels — particularly if you’re the sporty type. You need sufficient collagen to improve your performance and protect your joints from damage And like any protein, if you’re not replenishing collagen you’re losing it.
What’s the best substance to consume for additional collagen-building materials? The answer is collagen itself. Collagen is found naturally in many foods, including bony fish and bone broth. But in today’s world, it is hard to find pure collagen foods due to over-processing. One of the best alternatives is adding a collagen supplement your diet. For those who are more concerned about the function of collagen in the skin, Body Kitchen offers pure Collagen Di-Peptides capsules and powder. These contain Body Kitchen’s patented collagen formula with three times the di-peptides of conventional collagen, as well as age-defying resveratrol for youthful skin.
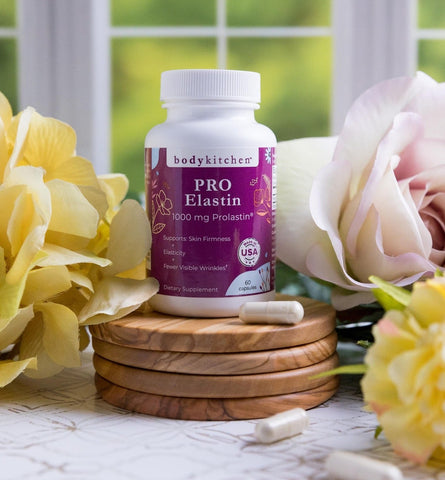
If you want to take your beauty and wellness to the next level, learn about Body Kitchen’s Pro-Elastin helps support the action of collagen by encouraging the body to produce more of the key protein elastin.
For best results, when taking any supplement, you should eat a healthy and varied diet too. This will ensure an adequate supply of the nutrients that your body needs to make full use of those additional collagen peptides.